Problem 1:
A static charge distribution produces a radial electric field
E = (A/r2)exp(-br) er.
where A and b are constants.
(a) What is the charge density? Sketch it.
(b) What is the total charge Q?
Problem 2:
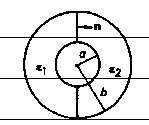 One half of the region between
the plates of a spherical capacitor of inner and outer radii a and b is filled
with a linear isotropic dielectric of permittivity ε1 and the other
half has permittivity ε2, as shown in
figure. If the inner plate has total charge Q and the outer plate has total
charge -Q, find
One half of the region between
the plates of a spherical capacitor of inner and outer radii a and b is filled
with a linear isotropic dielectric of permittivity ε1 and the other
half has permittivity ε2, as shown in
figure. If the inner plate has total charge Q and the outer plate has total
charge -Q, find
(a) the electric displacements D1 and D2
in the region of ε1 and ε2,
(b) the electric fields in the region of ε1 and ε2,
(c) and the total capacitance of this system.
Problem 3:
A parallel plate capacitor has square plates of width w and plate separation d.
A square dielectric also of width w and thickness d, with permittivity ε and
mass m, is inserted between the plates a distance x into the capacitor and held
there. The plates are connected to a battery with battery voltage V0.
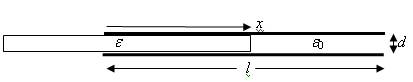
(a) Derive a formula for the force exerted on the dielectric as a function of x
Neglect edge effects.
Assume that the battery stays connected and the dielectric is released from rest
at x = w/2. Describe its subsequent motion.
What is the range of the dielectric's motion,
and within that range, what is the dielectric's speed as a function of position x?
What is the maximum speed vmax of the dielectric?
Express your answers in terms of ε0, ε, V0, w, d and m.
(Neglect friction, ohmic heating, radiation.)
(b) Now assume that the dielectric is released from rest at x = w/2 after the battery has been disconnected.
Derive a formula for the force exerted on the dielectric for w/2 < x < w. Neglect edge effects.
What is the maximum speed of the dielectric?
Express your answer in terms of ε0, ε, V0, w, d and m.
(c) Find the ratio vmax(case a) to vmax(case b) in
terms of ε0 and ε.
Problem 4:
A long straight wire is connected to an ideal battery. When the room
temperature is 20.0 oC, the established temperature of the wire is
22.0 oC.
The wire is disconnected and one-third of it is cut off. The remaining
piece of the wire is then connected to the same battery in the same room.
What is the new established temperature of the wire?
Assume Newton's law of cooling applies, i.e. the rate at which a system
transfers heat to its environment is proportional to the temperature difference
between the system and its environment.
 One half of the region between
the plates of a spherical capacitor of inner and outer radii a and b is filled
with a linear isotropic dielectric of permittivity ε1 and the other
half has permittivity ε2, as shown in
figure. If the inner plate has total charge Q and the outer plate has total
charge -Q, find
One half of the region between
the plates of a spherical capacitor of inner and outer radii a and b is filled
with a linear isotropic dielectric of permittivity ε1 and the other
half has permittivity ε2, as shown in
figure. If the inner plate has total charge Q and the outer plate has total
charge -Q, find