Problem 1:
A long coaxial cable carries a uniform volume charge density ρ on the inner
cylinder (radius a), and a uniform surface charge density on the outer
cylindrical shell (radius b). This surface charge is negative and is of just
the right magnitude that the cable as a whole is electrically neutral.
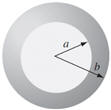
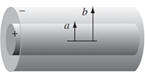
(a) Find the electric field inside the inner cylinder (r < a).
(b) Find the electric field between the cylinders (a < r < b).
(c) Find the electric field outside the cable (r > b).
Solution:
- Concepts:
Gauss' law - Reasoning:
The problem has enough symmetry to find E(r) from Gauss' law alone.
Choose cylindrical coordinates. Then E will only have a radial component,
E = E(r) (r/r). - Details of the calculation:
r < a: E*2πr* l = Qinsidel/ε0 = ρπr2l/ε0. E(r) = ρr/(2ε0) er.
a < r < b: E*2πr = ρπa2l/ε0. E(r) = ρa2/(2ε0r) er.
r > b: E(r) = 0.
Problem 2:
Two large parallel metal plates of area A are separated by a
distance d, small compared to the size of the plates. The distance d is small enough that the
plates can be treated as if they were infinite in extent. A battery
maintains a potential difference V across the plates. An external agent
slowly inserts an uncharged conducting slab of the same area A and thickness d/2 is
midway between the two plates, not touching either of them. After the slab
has been inserted, it is held in place at rest.
(a) What is the capacitance of the configuration before and after the slab
is inserted?
(b) How much work was done by the external agent inserting the slab?
Solution:
- Concepts:
Capacitance, energy and work - Reasoning:
We must find the ΔWmech, the work done by the external agents as the slab is inserted into a capacitor and the capacitance changes. - Details of the calculation:
(a) After the slab has been inserted, we have two parallel plate capacitors in series.
For these capacitor we have
C1 = C2 = ε0A/(d/4).
Cbefore = ε0A/d. 1/Cafter = 1/C1 + 1/C2. Cafter = 2ε0A/d.
(b) Total energy store in the capacitor: U = ½CV02.
Let ΔC = Cafter - Cbefore = ε0A/d.
ΔWmech + ΔWbat = ΔU. ΔWbat = ΔQV = ΔCV2. ΔU = ½ΔCV2.
ΔWmech = -½ΔCV2 = -½ε0AV2/d.
The external agent did negative work.
Problem 3:
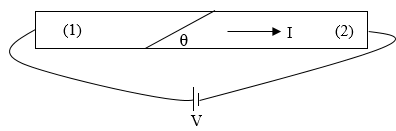
A very long, straight wire with circular cross section A is made from two
different materials with permittivities ε1 and ε2 and
conductivities σ1 and σ2, respectively, spliced together
at an angle θ. The wire is connected to a battery, and a current I flows in the wire.
Assume the microscopic form of Ohm's law holds in each material. Assume
the current density is uniform over a cross-sectional area of the wire.
(Since the wire is very long, the geometry of the ends can be ignored.)
(a) What is the free charge density at the splice?
(b) What is the bound charge density at the splice?
(c) What is the bound charge density at the splice on the material 2 side?
Solution:
- Concepts:
Ohm's law, Gauss' law - Reasoning:
j = σE, (D2 - D1)∙n2 = βfree, (E2 - E1)∙n2 = βtotal/ε0.
(Denote the surface charge density by β, since the symbol σ is already in use.) - Details of the calculation:
(a) j = I/A. ∇∙j = 0, there are no sources or sinks. j1∙n2 = j2∙n2 = j sinθ.
(D2 - D1)∙n2 = βfree, (ε2E2 - ε1E1)∙n2 = βfree, ((ε2/σ2)j - (ε1/σ1)j)∙n2 = βfree.
βfree = (ε2/σ2 - ε1/σ1) (I sinθ)/A.
(b) βtotal = (ε0/σ2 - ε0/σ1) (I sinθ)/A.
βbound = βtotal - βfree = -((ε2 - ε0)/σ2 - (ε1 - ε0)/σ1) (I sinθ)/A.
(c) P2 = ε0χ2E2 = (ε2 - ε0)E2. P2∙n2 = βbound(2).
βbound(2) = -(ε2 - ε0)(I sinθ)/(Aσ2).
βbound(1) = (ε1 - ε0)(I sinθ)/(Aσ1).