More Problems
Problem 1:
Consider a system of N particles with only 2 possible energy levels separated by ε. Let the ground state energy be zero. The system occupies a fixed volume V and is in thermal equilibrium with a reservoir at temperature T. Ignore interactions between particles and assume Boltzmann statistics apply.
(a) What is the partition function Z for a single particle in the system?
(b) What is the partition function ZN for the N-particle system?
(c) What is the average energy per particle?
(d) Show that the internal energy of the system can be written as U = -∂ln(ZN)/∂β,
with β = 1/(kBT)).
(e) The Helmholtz free energy is defined as F = U - TS, where U is the
internal energy of the system, T is the absolute temperature of the
surroundings, modelled as a heat bath, and S is the entropy of the system. For
the system under consideration dF = -PdV - SdT, S = -∂F/∂T.
Assume F = -NkT ln(Z). Find S and show that F = U - TS.
Solution:
- Concepts:
Boltzmann statistics, the partitiaon function - Reasoning:
In thermodynamic equilibrium P(Ei) ∝ giexp(-Ei/(kT).
Here the degeneracy gi is 1 for all i. - Details of the calculation:
(a) P(E) = Cexp(-E/(kBT)).
ΣjP(Ej) = CΣjexp(-Ej/(kBT)) = 1, C = 1/Σjexp(-Ej/(kBT)) = 1/Z.
Here Z = 1 + exp(-βε).
(b) ZN = (1 + exp(-βε))N.
(c) <ε> = ε exp(-βε)/Z = ε exp(-βε)/(1 + exp(-βε)).
(d) U = N<ε> = Nε exp(-βε)/Z = -N ∂ln(Z)/∂β = -∂ln(ZN)/∂β.
(e) If F = -NkT ln(Z), then S = -∂F/∂T = Nk ln(Z) + (NkT/Z) ε exp(-βε) (1/kT2)
= Nk ln(Z) + (N/Z) (ε/T) exp(-βε).
U - TS = (N/Z)ε exp(-βε) - (N/Z) ε exp(-βε) - NkTln(Z) = F
Problem 2:
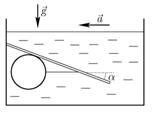 A hollow ball with a volume V is held in place in a tank under water by a
wire under a sloped plank as shown in the figure. The water density is ρ and average ball density is ρ/5.
The plank makes an angle α with the horizontal, with tan(α) = 1/3. What is the tension in the wire if
the whole system is accelerating horizontally with acceleration a = g/6.
A hollow ball with a volume V is held in place in a tank under water by a
wire under a sloped plank as shown in the figure. The water density is ρ and average ball density is ρ/5.
The plank makes an angle α with the horizontal, with tan(α) = 1/3. What is the tension in the wire if
the whole system is accelerating horizontally with acceleration a = g/6.
Solution:
-
Concepts:
Free-body diagrams, buoyancy - Reasoning:
Let the x-axis point towards the right and the y-axis point up. For the net force F on the ball we have Fy = 0, Fx = -ma. - Details of the calculation:
The buoyant force acting on the ball is Bt = ρVg j - ρVa i.
The buoyant force is the force the surrounding water would have to exert on the displaced water to accomplish the state of motion given in the problem in the absence of the object.
Fy = -mg + By - Ncosα = -ρVg/5 + ρVg - Ncosα = 4ρVg/5 - Ncosα = 0.
N = 4ρVg/(5cosα).
Fx = -Nsinα + T + Bx = -ma.
T = -ρVg/30 + 4ρVg/15 + ρVg/6 = 2ρVg/5.
Problem 3:
Two identical bodies with temperature-independent heat capacities C0 are initially at different temperatures T1 and T2. A Carnot cycle is run between them (with infinitesimal steps) until they have a common temperature TF. What is the value of TF?
Solution:
- Concepts:
Carnot Cycle - Reasoning:
For the Carnot cycle ΔStotal = 0. - Details of the calculation:
ΔStotal = ∫T1Tf dT m C0/T + ∫T2Tf dT m C0/T = 0.
∫T1Tf dT/T + ∫T2Tf dT/T = 0. ln(Tf/T1) + ln(Tf/T2) = 0. ln(Tf2/(T1T2)) = 0. Tf2/(T1T2) = 1.
Tf = (T1 T2)½.
Problem 4:
How much work does one mole of monoatomic ideal gas do during adiabatic
expansion when its volume increases by a factor of 2?
The gas is initially at room temperature T = 294 K and has three translational
degrees of freedom. Consider the expansion to be quasistatic. Calculate your
answer in Joules. How much does the entropy of the gas change? The ideal gas
constant is R = 8.31 J/(K mol).
Solution:
- Concepts:
Adiabatic expansion - Reasoning:
For an adiabatic process dQ = 0.
For an ideal gas PV = nRT. - Details of the calculation:
For an adiabatic process dU = -dW = -PdV.
But we also have U = n(3/2)RT. Here n = 1.
Therefore we have U = (3/2)PV,
dU = (3/2)(PdV + VdP).
Equating our two expressions for dU we have -PdV = (3/2)(PdV + VdP),
dP/P + (5/3)dV/V = 0. PV5/3= constant, (PV)V2/3= constant,
TV2/3= constant.
Tf/Ti = (Vi/Vf)2/3, Ui - Uf = (3/2)R(Ti - Tf) = (3/2)RTi(1 - (Vi/Vf)2/3) = (3/2)*8.31 *294*(1 - 0.52/3)
W = 3664 .7 J
Or:
W = ∫ViVfPdV = R∫ViVf(T/V)dV = RTiVi2/3∫ViVfV-5/3dV = -(3/2)RTiVi2/3(1/Vf2/3 - 1/Vi2/3).
W = 3/2)RTi(1 - ( Vi/Vf)2/3) = 3664 .7 J
The entropy does not change, dS = dQ/T = 0.