Problem 1:
A charged metal sphere with charge +Q and radius 'a' is positioned at the
center of a neutral, spherical metal shell with inner radius 'b' and outer
radius 'c'.
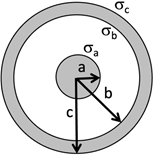
(a) Calculate the surface charge densities σa, σb,
σc
on the inner sphere, the inner surface of the shell, and the outer surface of
the shell, respectively.
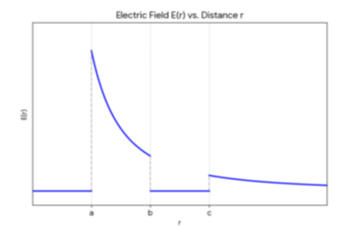
(b) Calculate the electric field E everywhere, and sketch E vs Radius.
(c) Calculate the potential V(0) at the center of the inner sphere. Use the
usual convention of a reference point of infinity V(∞) = 0.
Solution:
- Concepts:
Gauss' law
- Reasoning:
The field due to a spherically symmetric charge
distribution can be found from Gauss' law.
- Details of the calculation:
-
(a) The problem has spherical symmetry. In electrostatics E = 0 inside of a
conductor.
Surface charge density on surface with radius a: σa = Q/(4πa2)
Surface charge density on surface with radius b: σb = -Q/(4πb2)
Surface charge density on surface with radiusc2: σc =
Q/(4πc2)

(b) Gauss' law: E = E(r)(r/r) due to the
spherical symmetry.
r > c: E(r) = Q/(4πε0r2).
b < r < c: E = 0.
a < r < b: E(r) = Q/(4πε0r2).
r < a: E = 0.
(c) V(∞) = 0.
r > c: V(r) = Q/(4πε0r).
b < r < c: V(r) = Q/(4πε0c).
a < r < b: V(r) = Q/(4πε0c) + ∫rb dr Q/(4πε0r2)
= (Q/(4πε0))[1/c + 1/r - 1/b].
r < a: V(r) = Q/(4πε0))[1/c + 1/a - 1/b] = Q/(4πε0))(ab +
bc -ac)/(abc).
V(0) = Q/(4πε0))(ab + bc -ac)/(abc).
Problem 2:
A point charge q is placed a distance a from a
grounded, infinite conducting plane. Find the induced surface charge density.
Solution:
- Concepts:
Method of images
- Reasoning:
Put the point charge on the z-axis. The electric field
above the xy-plane is the superposition of the field of a point charge q at z =
a and a point charge -q at z = -a on the z-axis.
- Details of the calculation:
At z = 0 we have at a distance r away from the origin
E = 2kqa/(a2 + r2)3/2,
pointing in the negative z-direction.
The surface charge density is σ = -ε0E = -ε02kqa/(a2
+ r2)3/2 = -(qa/(2π))/(a2
+ r2)3/2.
Problem 3:
A small conducting ring of radius a is located in the xy-plane centered at
the origin. A positive charge Q is place on the ring.
(a) Find the potential Φ on the z-axis at z > a and expand your
expression in powers of a/z.
(b) The potential Φ(r,θ) at a arbitrary points in space with r >
a can be
expanded in terms of Legendre polynomials, Φ(r,θ) = ∑n=0∞[Anrn
+ Bn/rn+1]Pn(cosθ).
Find the expansion coefficients.
Solution:
- Concepts:
Symmetry, Φ(r,θ) = ∑n=0∞[Anrn
+ Bn/rn+1]Pn(cosθ) is the
general solution to Laplace's equation for problems with azimuthal symmetry.
- Reasoning:
Φ(r) = [1/(4πε0)]∫ρ(r')dV'/|r -
r'|.
We can evaluate this integral for r = rk.
For r > a, Φ(r) satisfies Laplace's equation, ∇2Φ(r) =
0. The general solution is
Φ(r,θ) = ∑n=0∞[Anrn + Bn/rn-1]Pn(cosθ).
We can find the coefficients by comparing the general solution to the solution
found by integration on the z-axis.
- Details of the calculation:
(a) Φ(z) = [1/(4πε0)]Q/(a2 + z2)½.
Expanding (a2 + z2)-½ = (1/z)(1 + a2/z2)-½
= (1/z)(1 - ½a2/z2 + ½(3/2)a4/z4
- ½(3/2)(5/2)a6/z6 + ...)
= (1/z)(1 + ∑n=1∞(-1)n(a/z)2n(2n - 1)!!/2n).
Φ(z) = [Q/(4πε0z](1 + ∑n=1∞(-1)n(a/z)2n(2n - 1)!!/2n).
(b) For r > a ∑n=0∞(Bn/rn+1)Pn(cosθ).
Only the even parity terms contribute and all An are zero since Φ = 0
at infinity.
We can therefore write Φ(r,θ) = ∑n=0∞(B2n/r2n+1)P2n(cos(θ)).
On the positive z-axis Φ(z) = ∑n=0∞(B2n/z2n+1),
since Pn(1) = 1 for all n.
Equating the two expressions for Φ(z), we
have
Φ(z) = ∑n=0∞(B2n/z2n+1) =
[Q/(4πε0)](1/z + ∑n=1∞(-1)n(a2n/z2n+1)(2n
-1)!!/2n).
Equating term with equal powers of z we have B0 = Q/(4πε0),
B2n≠0 = [Q/(4πε0)](-1)na2n(2n -1)!!/2n.
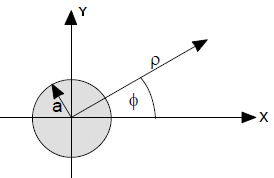
Problem 4:
The z-axis is the symmetry axis of a very long cylinder of radius a, made
from dielectric material of relative permittivity ε = Kε0. The
cylinder carries a free surface charge density σfree = σf0cosφ.
The electric field inside and outside the cylinder is of the form
Ein = -A1i = -A1cosφ (ρ/ρ)
+ A1sinφ (φ/φ),
Eout = (A2cosφ (ρ/ρ) + A2sinφ (φ/φ))/ρ2.
Use the boundary conditions conditions for E and D to find the
polarization P of the cylinder in terms of K and σf0
Solution:
- Concepts:
Boundary conditions for the electric field and the electric displacement
- Reasoning:
The given Ein and Eout can satisfy the
boundary conditions. The constants A1 and A2 for
which the boundary conditions are satisfied are unique. Given Ein,
we can find P.
- Details of the calculation:
Boundary conditions:
(E2 - E1)∙n2
= (σ/ε0),
(E2 - E1)∙t
= 0, (D2
- D1)∙n2
= σf.
(Eout -
Ein)∙t = 0 --> A1
= A2/a2, Ein = (-A2cosφ (ρ/ρ)
+ A2sinφ (φ/φ))/a2.
(Dout -
Din)∙nout
=
σfree --> ε0A2/a2 + εA2/a2
= σf0, A2 = σf0a2/(ε0
+ ε).
Ein = -A1i = σf0/(ε0
+ ε)i.
P = ε0χeEin = ε0(K -
1)Ein = -ε0(K - 1)σf0/(ε0
+ ε)i = -[(K
- 1)/(K
+ 1)] σf0i.Or we can use
(Eout
- Ein)∙nout
= σ/ε0 = (σfree + σbound)/ε0
--> A2 = (σf0 + σb0)a2/(2ε0),
where σbound = σb0cosφ.
σf0/(ε0 +
ε) = (σf0 + σb0)/(2ε0), [(ε0 -
ε)/(ε0 + ε)]σf0 = [(1 - K)/(1 + K)]σf0 = σb0.
On the x-axis at x = a, P∙n = P = σb0.
Therefore
P = -[(K - 1)/(K + 1)]σf0i.


