The program calculates the differential cross section for the elastic scattering of electrons from neutral Argon targets. The method used is the same as described in program 3. To do the integration we need to know the potential V(r). Garvey, Jackman, and Green have numerically calculated independent-particle-model potentials for atoms and ions using multi-configuration Hartree-Fock wavefunctions. [1] We obtain our potential from their paper.
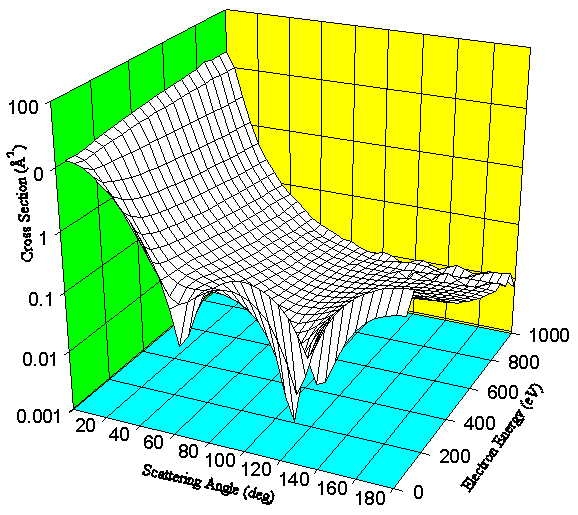
Figure 1 shows the doubly-differential elastic scattering cross section s(q,E) of electrons from Ar for electron energies from 50 to 1000eV and for scattering angles from 5o to 180o. For large electron energies the cross sections decrease smoothly with scattering angle but for smaller energies they show considerable structure. The more the potential of the atom differs from the simple Coulomb potential of a bare nucleus, the more structured is the doubly-differential electron scattering cross sections.

Figure 1
For electrons with energies ranging from 20 to 800eV and Argon targets experimental data are readily available for comparison with our results. In figures 2 we compare the calculated cross sections at 200eV and 800eV for Ar targets with experimentally measured cross sections for the same electron energies and targets. [2] The calculations agree well with the experimental data.
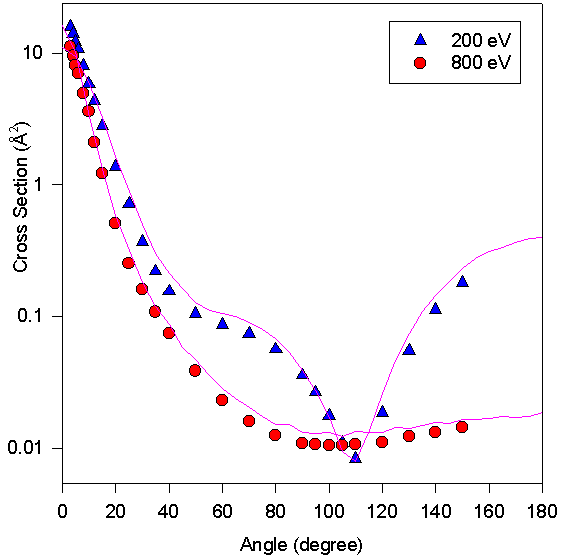
Figure 2
References:
[1] R. H. Garvey, C. H. Jackman, and A. E. S. Green, Phys. Rev. A 12,
1144 (1975)
[2] R. D. DuBois and M. E. Rudd, J. Phys. B 9, 2657 (1976)